Python RAG API Tutorial with LangChain & FastAPI – Complete Guide
A hands-on guide to building a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) API using Python, LangChain, FastAPI, and pgvector — complete with architecture diagrams and code.
Introduction
Original article on my website: Python RAG API Tutorial with LangChain & FastAPI – Complete Guide
During last few months I was observing new releases in AI sector and new startups which are using AI. So I was curious what they are doing? How they are doing these AI things? While I have some experience with building AI applications I feel that's it's not enough and I want to know more about building AI apps. That's why with this new blog post I'm starting a new journey in my life - blogging about software engineering.
In this blog post I will explain how to build AI powered application to chat with uploaded PDF files. It will use these techniques and frameworks:
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
LangChain to build RAG and communicate with OpenAI
FastAPI to build API
Python 😊
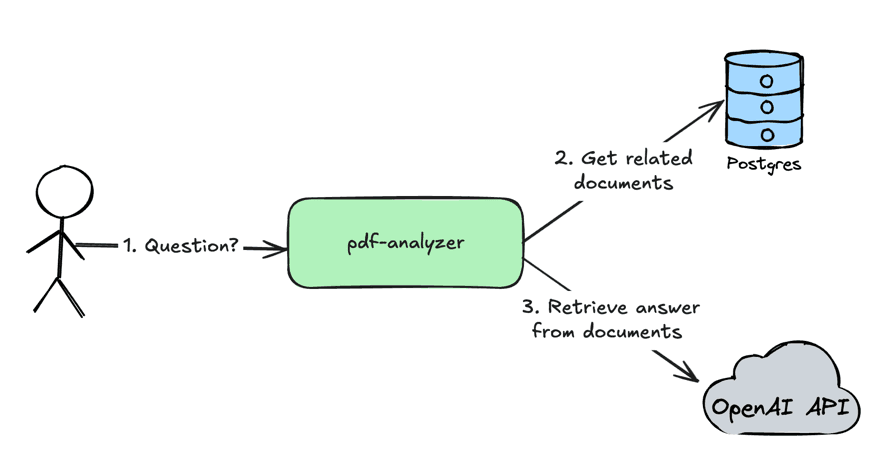
High Level Architecture
pdf-analyzer - service which analyzes PDF documents and retrieves answers for user questions from PDF documents
User sends a question to the
pdf-analyzerserviceThe
pdf-analyzerservices gets related document to a user question from the Postgres databaseThe
pdf-analyzersends a request with a user question and retrieved documents from the step 2 to OpenAI API to get an answer for a user question.
Before we will jump to the details of implementation let's understand why this architecture has been called "retrieval augmented generation".
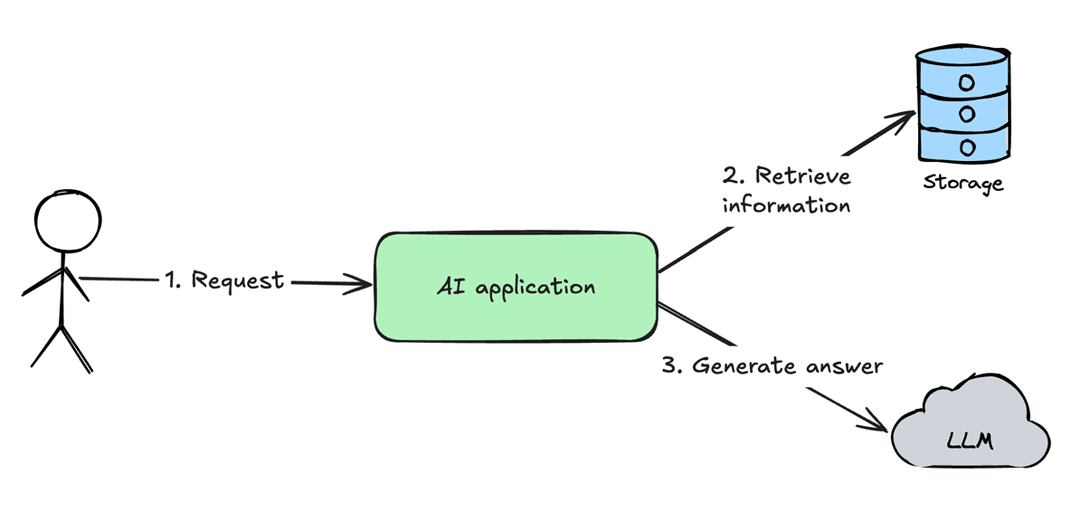
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) - the pattern in AI applications in which to provide an answer for a user am application will provide related information for a user request to LLM. Which will make LLM answer more "smarter" because LLM will get more context about a problem which it should solve.
So the process of RAG the best depicts this diagram:
User sends a request to AI application
AI application retrieves information from the external storage
AI application augments original user request with a retrieved information and sends to LLM to generate an answer
This approach results in much more better LLM responses than just directly send the document with a lot of pages to LLM and ask for a response.
Use Cases of RAG
Use case of the RAG pattern is to analyze information for cases when amount of information is higher than LLM context. While modern LLMs have huge context size RAG pattern can still be a benefit because if LLM context is filled more than 50% the chances of hallucinations are very high. So to get the best responses from LLM need to keep context usage minimal.
Use Cases of RAG in the real world
In the real world RAG can be used in these applications:
AI Chat with company documentation
Customer Support AI Bot
Frequent retrieval of information from unstructured data
Middle step of more complex flow
That's it from the theory and let's jump to the implementation part 😎
Implementation
User Flows
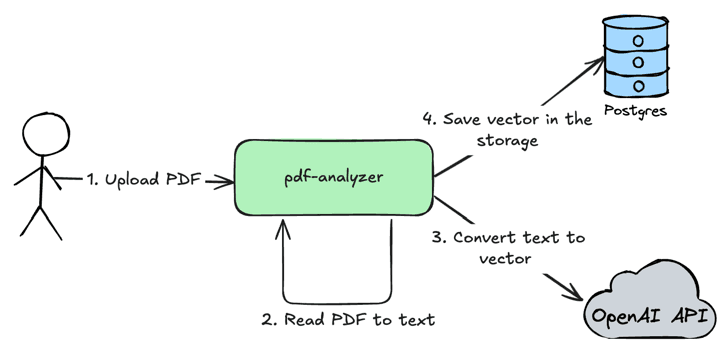
Upload PDF document
User uploads PDF document in the
pdf-analyzerservice.The
pdf-analyzerservice reads PDF to text, splits text by chunks to increase accuracy of data retrieval.The
pdf-analyzerservice uses OpenAI API to convert text to a vector which will represent provided text chunk. Next we will use this vector to perform search in the database by using math.Save vector in the storage. So at this step we are saving numeric vectors of text and the text itself in the storage. Later we will use math to find the most relevant text chunks to a user question
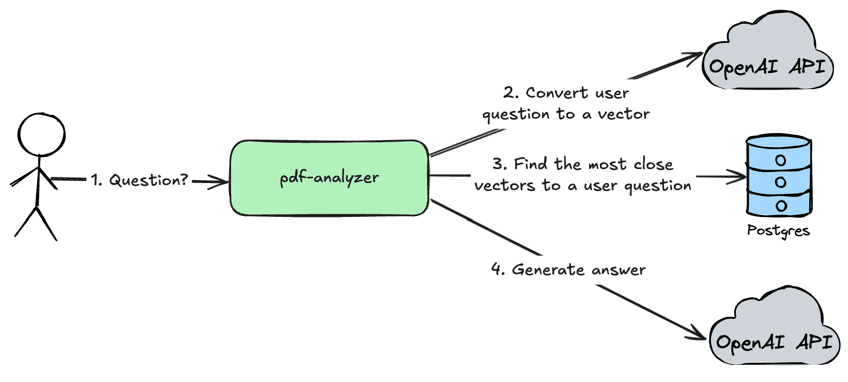
Chat with uploaded PDF document
User sends a question via API to the
pdf-analyzerserviceThe
pdf-analyzerservice converts user question to a numeric vector by using OpenAI APIThe
pdf-analyzerservice finds the most close vectors in the storage for a user question.The
pdf-analyzersends user question, retrieved documents and system prompt to the OpenAI API to get the most accurate answer
Technology Decisions
By knowing user flows above we can decide what technologies we will use to build this application.
LangChain Framework - the best framework to build AI systems which covers a lot of cases
Python - original language for LangChain is Python, so we will go with it
FastAPI - the modern and super convenient framework to build APIs in Python which can handle huge load. Also it allows to handle high load in Python.
Postgres - A mature database with a support of vector storage via plugin
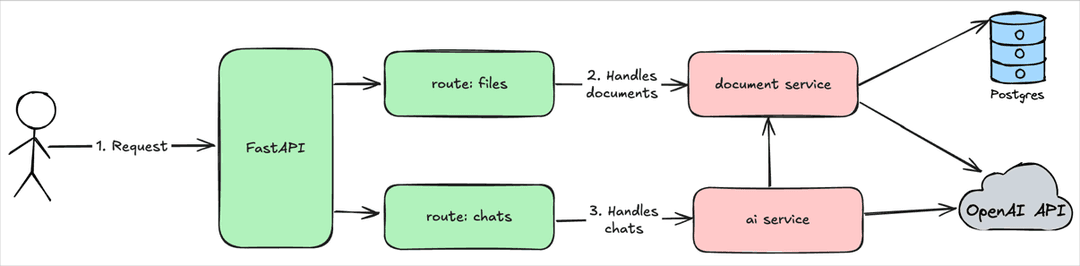
Service Architecture
The pdf-analyzer service will use a classical layered architecture:
Routes
filesandchatswill handle HTTP requests and use services to execute business logicServices
document serviceandai servicewill execute business logic and integrate with Postgres and OpenAI API
This architecture approach provides a possibility to satisfy single responsibility principle and keep system simple.
The whole source code of an article is available at GitHub. For a simplicity of an article I will include only code which highlights the most important concepts of RAG API.
Implementation
Document Service
DocumentService - the service which is responsible to save/read documents.
import tempfile
from langchain_core.vectorstores import VectorStore
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain_text_splitters.base import TextSplitter
from pdf_analyzer.models import File
from dataclasses import dataclass
from sqlmodel import Session
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
from pdf_analyzer.repositories.file import FileRepository
from uuid import UUID
@dataclass
class DocumentService:
vector_store: VectorStore
text_splitter: TextSplitter
file_repository: FileRepository
async def save(self, session: Session, file: File) -> File:
# 1. Save file to the database
file = self.file_repository.create_file(session, file)
# 2. Convert file to a list of LangChain documents
documents = self.__convert_to_documents(file)
# 3. Split list of LangChain documents to smaller documents to improve accuracy of RAG
all_splits = self.text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
# 4. Adds metadata to a file to allow communicate with specific file
self.__add_metadata(all_splits, file)
# 5. Save documents in the vector store
await self.vector_store.aadd_documents(all_splits)
return file
async def search(self, text: str, file_ids: list[UUID] = []) -> list[Document]:
documents_filter = None
if file_ids:
documents_filter = {
"file_id": {"$in": [str(file_id) for file_id in file_ids]}
}
return await self.vector_store.asimilarity_search(text, filter=documents_filter)
def __add_metadata(self, documents: list[Document], file: File):
for doc in documents:
doc.metadata["file_name"] = file.name
doc.metadata["file_id"] = str(file.id)
def __convert_to_documents(self, file: File) -> list[Document]:
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(suffix=".pdf", delete=True) as tmp_file:
tmp_file.write(file.content)
tmp_file.flush()
loader = PyPDFLoader(tmp_file.name)
return loader.load()The most interesting part of the system is this DocumentService which saves file in the database by following these steps:
Save file to the database
Convert file to a list of LangChain documents
Split list of LangChain documents to smaller documents to improve accuracy of RAG
Adds metadata to a file to allow communicate with specific file
Save documents in the vector store
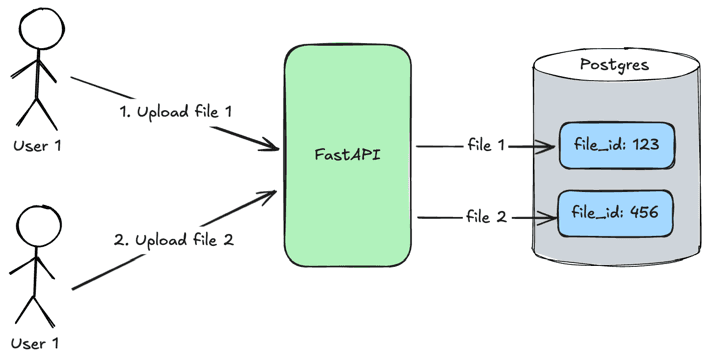
Pretty important step is step 4 because at the end our user wants to communicate with specific files and not all files in the system. That's why we are adding metadata tag file_id in the __add_metadata method.
User 1uploadsfile 1and the__add_metadatamethod specifiesfile_id: 123for itUser 2uploadsfile 2and the__add_metadatamethod specifiesfile_id: 456for it
When users will search relevant content in files they will pass file_id tag which will be used to find specific files as it was done in the search method.
AI Service
AIService - the service which is responsible for OpenAI LLM API integration.
from langchain_core.language_models import BaseChatModel
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
"You are an expert extraction algorithm. "
"Only extract relevant information from the text. "
"If you do not know the value of an attribute asked to extract, "
"return null for the attribute's value.",
),
("system", "{data}"),
("human", "{text}"),
]
)
class Output(BaseModel):
answer: str | None = Field(
default=None,
description="Answer on the question",
)
class AIService:
def __init__(self, llm: BaseChatModel):
self.llm = llm
self.structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(schema=Output)
def retrieve_answer(self, question: str, docs: list[Document]) -> str | None:
data = "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs)
prompt = prompt_template.invoke({"text": question, "data": data})
llm_result = self.structured_llm.invoke(prompt)
return Output.model_validate(llm_result).answer if llm_result else NoneThe retrieval of an answer from a document looks like this:
The list of LangChain documents joins together in a string
LangChain prompt template substitutes template variables and generates a final prompt
LangChain llm class generates a structured response
Outputby sending my prompt to OpenAILLM response validates to be a valid Pydentic
Outputmodel
ChatService
ChatService - the service which is responsible for a user conversation with LLM and augmenting user requests to LLM.
from dataclasses import dataclass
from pdf_analyzer.schemas import ChatCreate
from pdf_analyzer.repositories import ChatRepository, MessageRepository
from pdf_analyzer.models import Chat, Message, SenderType
from sqlmodel import Session, select
from pdf_analyzer.schemas import MessageCreate
from pdf_analyzer.services.ai import AIService
from pdf_analyzer.services.document import DocumentService
from uuid import UUID
from typing import Sequence
@dataclass
class ChatService:
chat_repository: ChatRepository
message_repository: MessageRepository
ai_svc: AIService
document_svc: DocumentService
def create_chat(self, session: Session, chat_create: ChatCreate):
chat = Chat(name="New Chat", files=[])
return self.chat_repository.create(session, chat, chat_create.file_ids)
def find_all_chats(self, session: Session):
return self.chat_repository.find_all(session)
def get_chat(self, session: Session, chat_id: UUID):
chat = session.exec(select(Chat).where(Chat.id == chat_id)).one_or_none()
if not chat:
raise ValueError(f"Chat with ID {chat_id} does not exist.")
return chat
async def send_message(
self, session: Session, chat_id: UUID, message_create: MessageCreate
):
human_message = Message(
content=message_create.content,
chat_id=chat_id,
sender_type=SenderType.HUMAN,
)
chat = self.get_chat(session, chat_id)
docs = await self.document_svc.search(
human_message.content, [file.id for file in chat.files]
)
answer = self.ai_svc.retrieve_answer(
human_message.content,
docs,
)
if not answer:
answer = "N/A"
ai_message = Message(content=answer, chat_id=chat_id, sender_type=SenderType.AI)
self.message_repository.save_messages(session, human_message, ai_message)
return ai_message
def find_messages(self, session: Session, chat_id: UUID) -> Sequence[Message]:
return self.message_repository.find_by_chat_id(session, chat_id)The most interesting method is send_message which is doing:
Gets chat by message id
Gets documents related to a chat
Sends a request to LLM with user request and retrieved documents
Save user message and AI response
Return a response to a user
Testing
0. Install dependencies
To run this project Poetry should be installed in the system.
poetry install- installs dependenciespoetry shell- uses virtualenv Python in this shell
1. Create .env file
Let's test this API by hands to see how it works. The code is available in GitHub so you can clone a repository and run code locally. Need to create .env file with specified variables:
PDF_ANALYZER_OPENAI_API_KEY- OpenAI API key.PDF_ANALYZER_DB_URL- Postgres connections string.Specify
postgresql://root:root@localhost:5432/pdf-analyzerif you will run Postgres from thedocker-compose.yamlfile.
2. Launch docker-compose.yaml
docker compose up -d - this will start Postgres with configured vector plugin in the Docker container.
3. Launch FastAPI server
Run this command to start FastAPI:
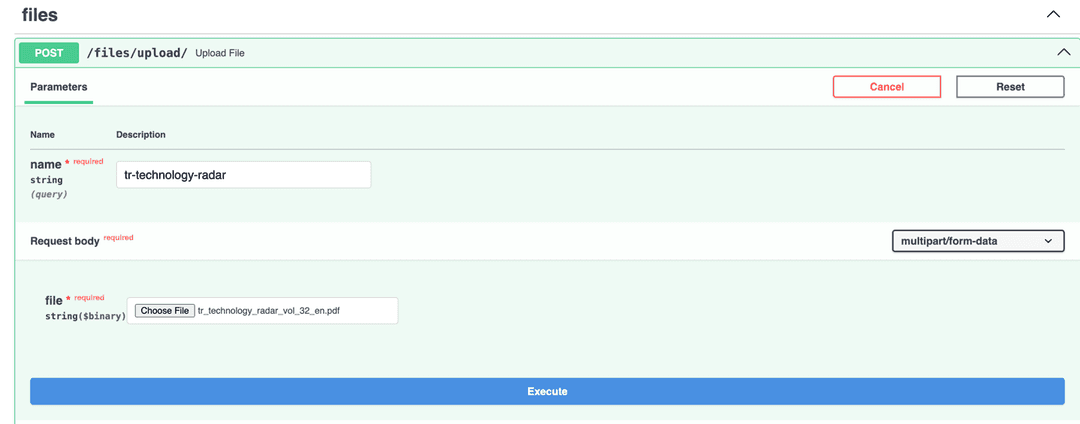
fastapi dev src/pdf_analyzer/main.py4. Upload a file
Open http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs#/files/upload_file_files_upload__post and upload any file. I will upload Technology Radar pdf in my example.
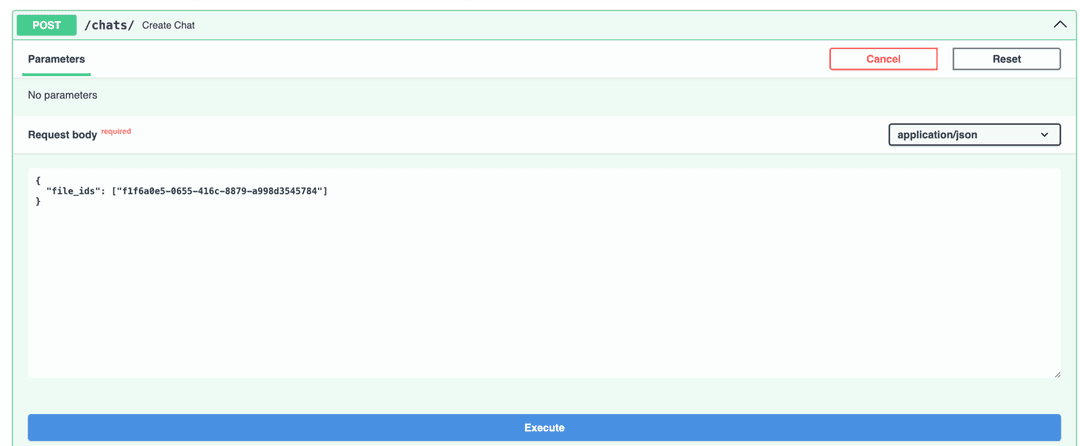
5. Create a chat
Open http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs#/chats/create_chat_chats__post and create a chat with using file id received in a response after file uploading.
6. Send a message
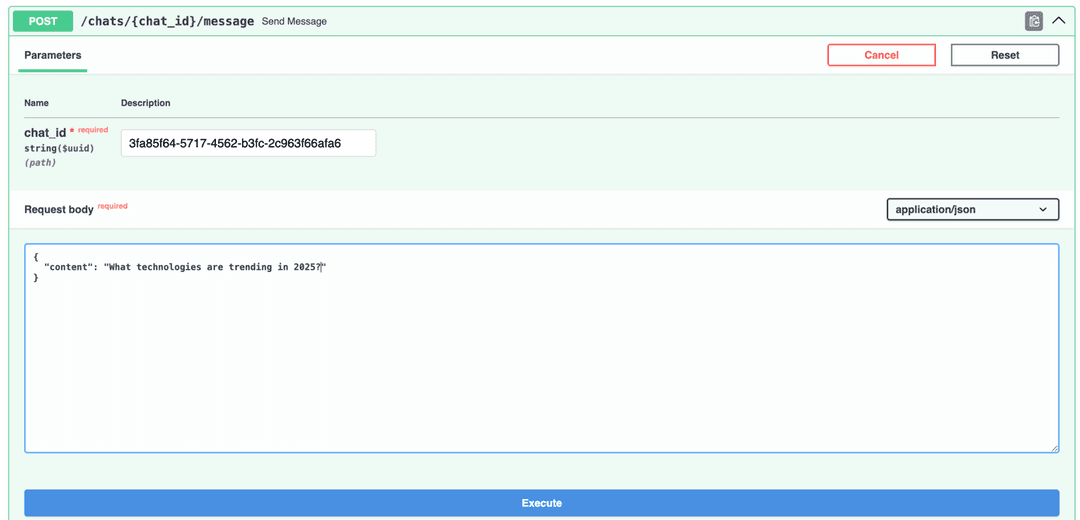
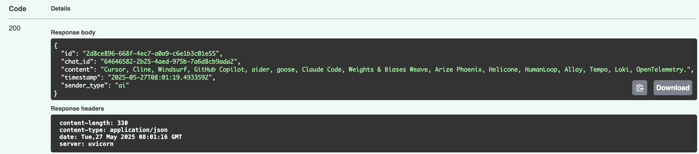
Open http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs#/chats/send_message_chats__chat_id__message_post and send a message to a chat to communicate with uploaded file.
There is a response:
Conclusions
In this article I highlighted how to build RAG API in Python with LangChain and FastAPI. The source code is available on GitHub. This RAG technique looks useful and I will look to integrate it with some real world applications.
Original article on my website: Python RAG API Tutorial with LangChain & FastAPI – Complete Guide